Reprogramming Cardiac Scar Tissue into Working Cardiomyocytes
A group of researchers have been looking into a way to permanently repair the heart after a heart attack and they believe they have found the solution. 50% of the cells in the heart are cardiac fibroblasts. The fibroblasts provide structural support for the heart, but after heart attacks the number of them increase due to formation of scar tissue. Through in vivo experiments with mice, the research has proven that a concoction of three transcription factors; Gata4, Mef2c and Tbx5 (GMT) will reprogram the fibroblasts in cardiomyocyte-like cells with cardiomycoyte-like gene expression, action potential, beating upon electrical stimulation, and electrical coupling. This concoction has also reduced the infarct size. The technology has not been tested in humans yet, but researchers are hopefully that the mix of transcription factors will prove to have similar affects in the human body.
This is a very interesting article to me because of the huge prevalence (increasingly so) of heart attacks. In the US alone, someone has a heart attack approximately every 25 seconds. Consequently, there is a growing number of people suffering from the post heart attack complications such as a poorly contracting heart due to scar tissue which has many health problems. The scar tissure makes your heart work harder to contract increasing the risk of another heart attack. Technology like this is very exciting because it would increase the patients outlook greatly and would have a large reach due to the amount of people that have this problem including members of my own family.
Article URL: http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v485/n7400/full/nature11044.html
This is a very interesting article to me because of the huge prevalence (increasingly so) of heart attacks. In the US alone, someone has a heart attack approximately every 25 seconds. Consequently, there is a growing number of people suffering from the post heart attack complications such as a poorly contracting heart due to scar tissue which has many health problems. The scar tissure makes your heart work harder to contract increasing the risk of another heart attack. Technology like this is very exciting because it would increase the patients outlook greatly and would have a large reach due to the amount of people that have this problem including members of my own family.
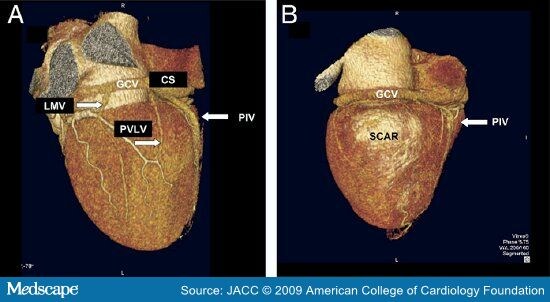 |
| Left: normal heart right: Scar Tissue on the heart after myocardial infarction |
Article URL: http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v485/n7400/full/nature11044.html
